Introduction to DOM
What is the DOM
- Document Object Model: structured representation of HTML documents
- allows JavaScript to access HTML elements and styles to manipulate them
- Connection between the HTML, CSS and JavaScript
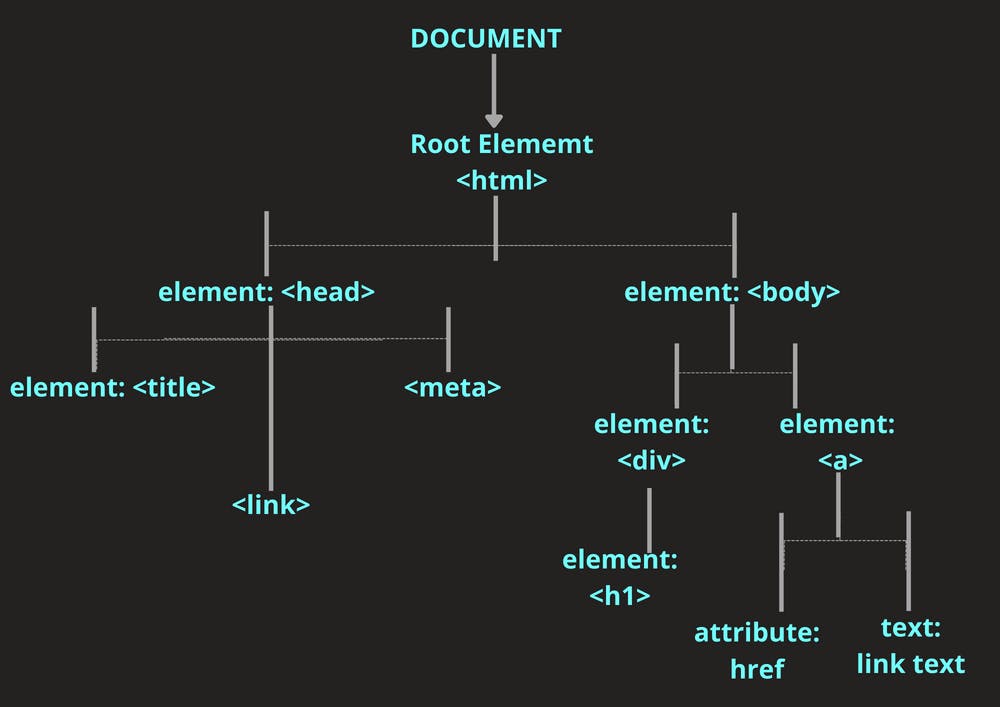
The DOM Tree Structure
- document is a special that is the entry point to the DOM doesn't only contain elements but what ever is in the HTML document
Example
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title> A simple Page </title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<h1> </h1>
</div>
<a href="#"> </a>
DOM And JavaScript
- DOM and DOM methods are part of the web API’s
- Web API are basically libraries written in JavaScript that are automatically available for us to uses
Manipulating DOM in the browser using JavaScript
Selecting Elements
- we can select DOM elements using the query selector
Syntax
document.queryselector("element")
- we use document object to access the HTML elements
- we use the
queryselectormethod, and we provide the HTML element using the CSS selector
Example
document.queryselector(".message")
Manipulating Elements
Manipulating HTML Elements
.textContent- we can access the content of a HTML element using the text Content method
document.queryselector(.message).textContent = "Hello, World!"
.value- for input values and other, we can access their value using the .value method
Manipulating CSS Elements
.styleUsing the style attribute, we can manipulate the CSS elements
Example
document.queryselector(".message").style.color="#353536"
Note
Nothing changes in the CSS file, rather these changes are added as attributes to the HTML file
<p class =message style="color: #454546"> Hello, World! </p>
Manipulating Classes
.classListaccess multiple methods to manipulate CSS classes
dice.classList.remove("hidden");
Handling click Events
.addEventListener- The event listener records any click activity
- syntax
document.querySelector("element").addEventListener("click", function () {}- the add event listener expects 2 arguments, the "click" and the function ()
- the function acts as a normal function
Handling Keyboard Events
.keydownrecords any event as soon as any key is pressed
document.addEventListener("keydown", function () { console.log("hello, world") });
Function with Parameter
After entering a parameter to the
keydownmethod we access the keyboard event objectUsing the keyboard object, we can access other methods and manipulate them
document.addEventListener("keydown", function (e) { if (e.key === "Escape" && !modal.classList.contains("hidden")) hideModal(); });

